Page breaks in HTML/CSS
Page breaks in HTML/CSS are critical for controlling how content is split across pages in printable formats. The CSS properties break-before, break-after, and break-inside are primarily used to manage these breaks.
Page Break Properties
break-before: This property adds a page break before an element. Defaultauto.break-after: This property adds a page break after an element. Defaultauto.break-inside: This property avoids a page break inside an element. Defaultauto.
Breaking Before an Element
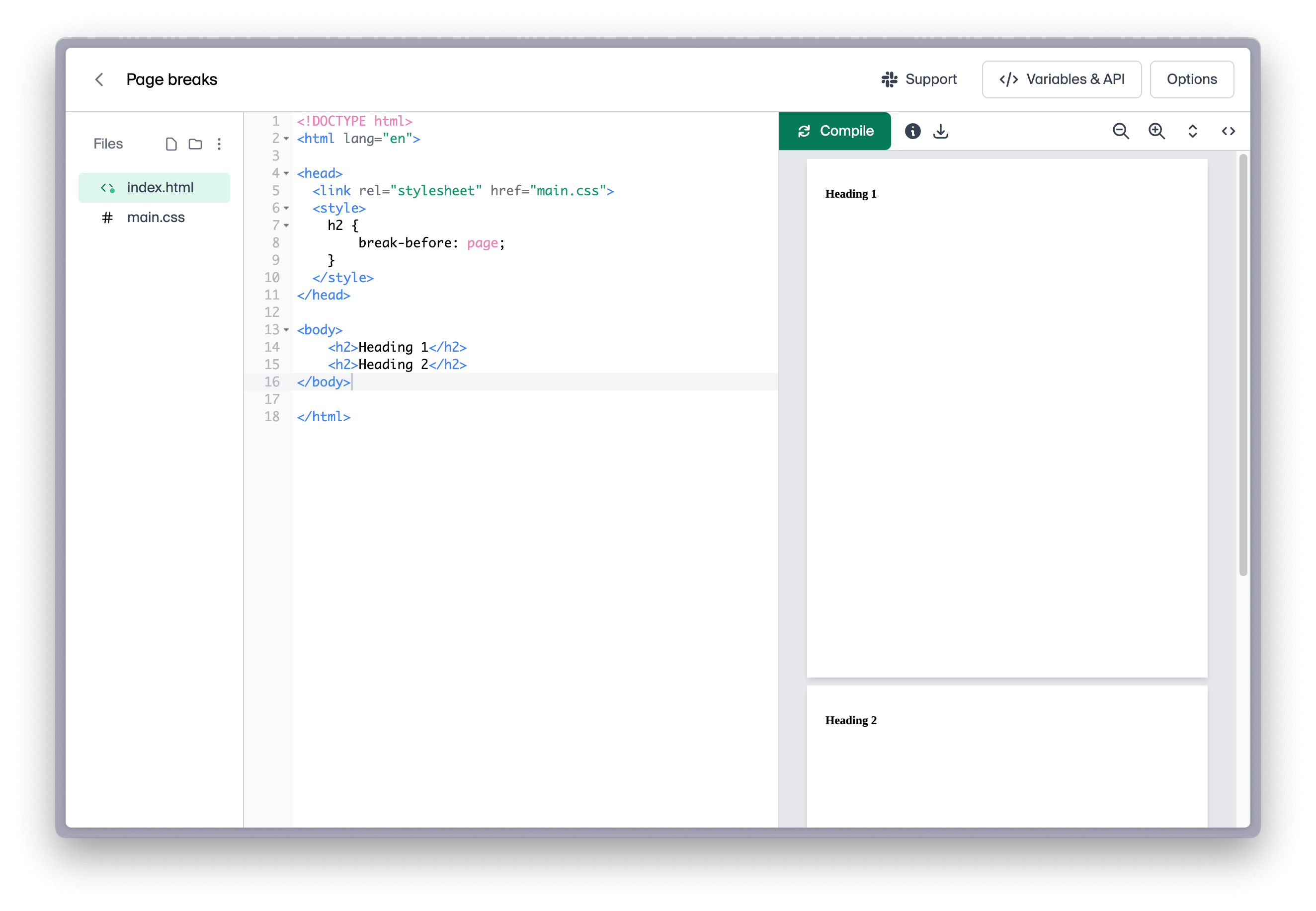
To add a page break before an element, you can use the page-break-before property. This can be useful when you want to ensure that a new section starts at the top of a new page.
CSS for adding breaks before elements
h2 {
break-before: page;
}
In the above example, a page break will always be added before each <h2> element.
Breaking After an Element
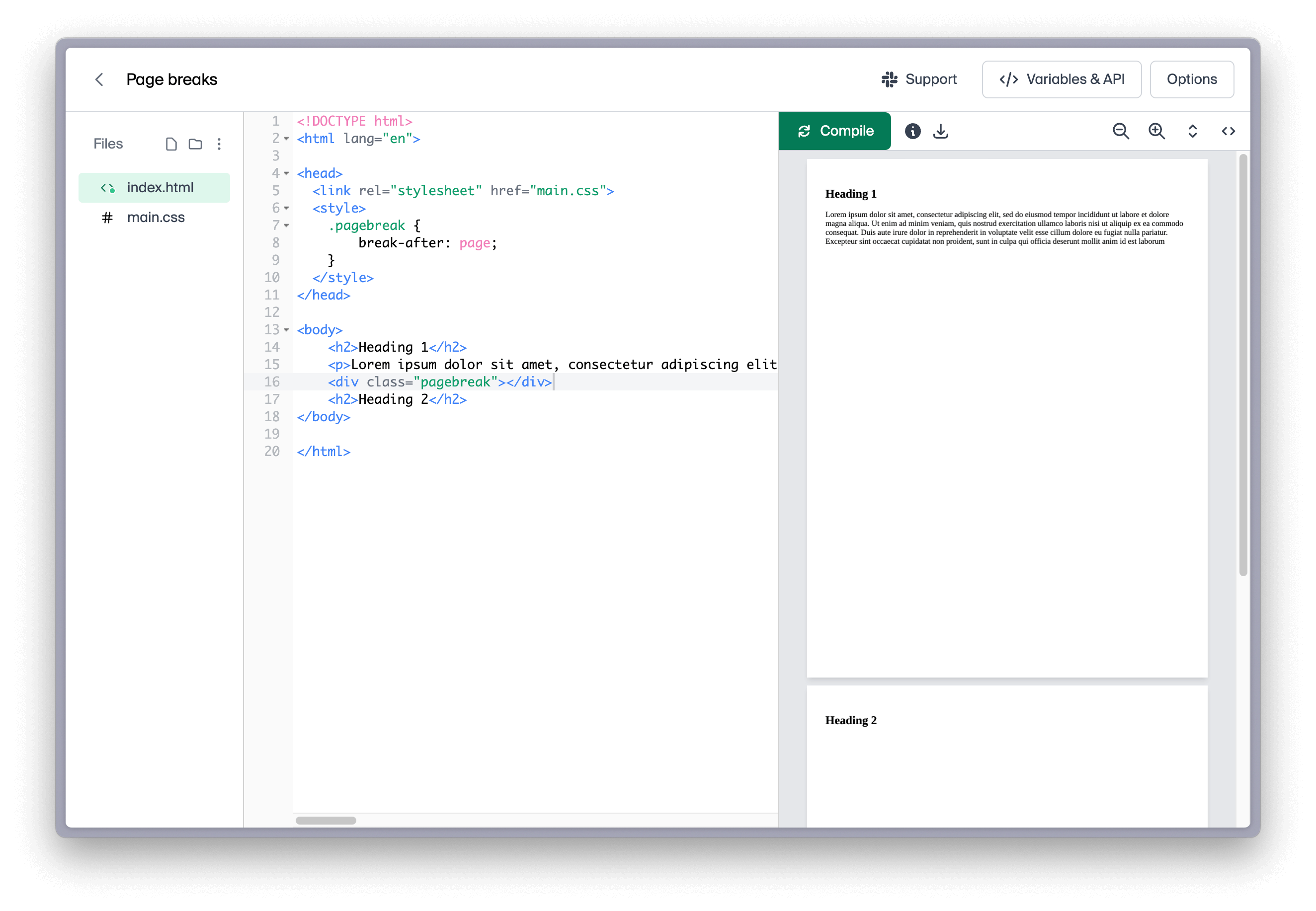
To add a page break after an element, you can use the break-after property. A common use-case for this is to create a custom pagebreak similar to <br /> but for breaking pages instead of lines.
CSS for adding breaks after elements
.pagebreak {
break-after: page;
}
Here's our custom pagebreak element in use:
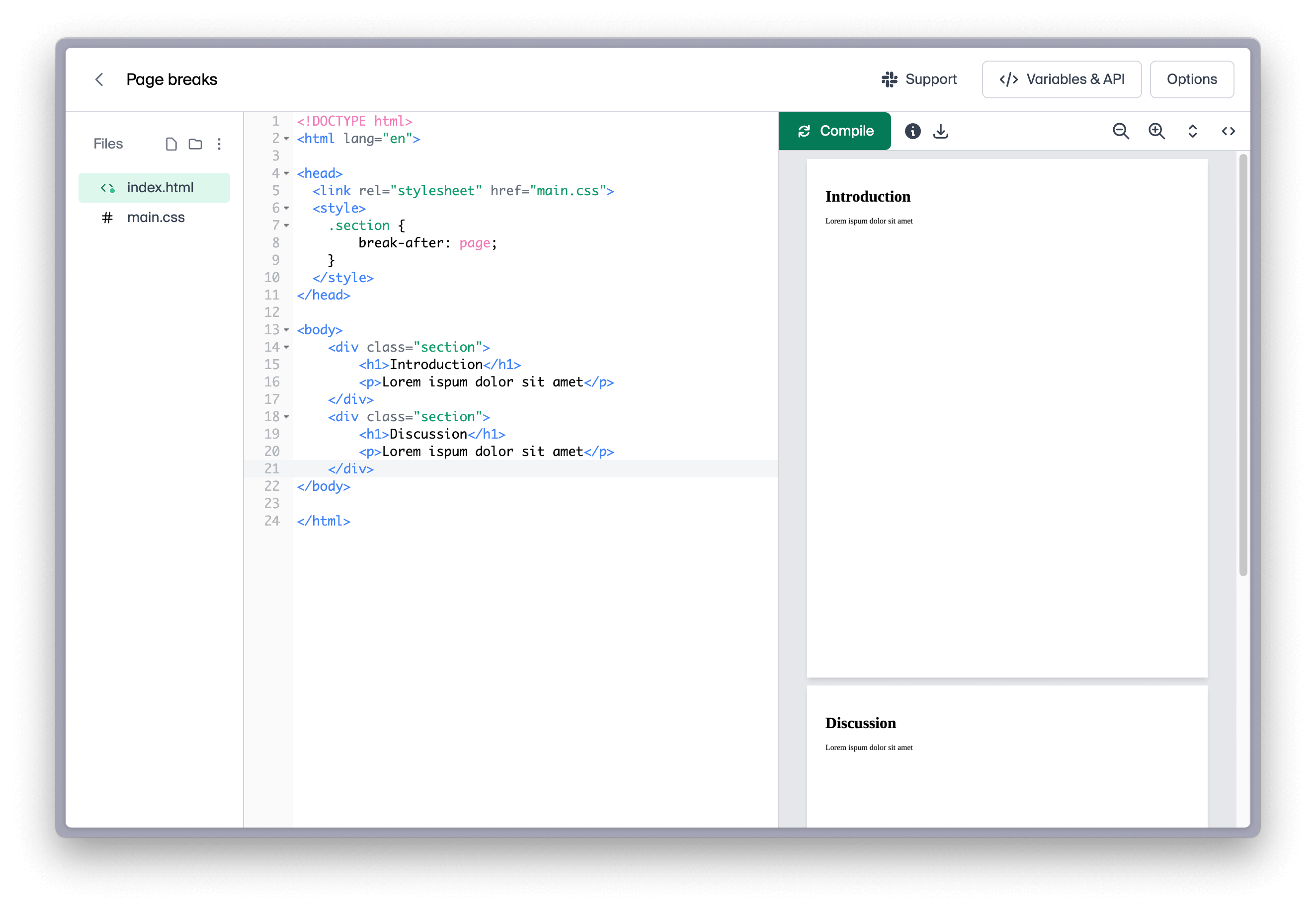
Alternatively, you can define a page/section wrapper component with this property to neatly divide your document.
Avoiding Breaks Inside an Element
To avoid a page break inside an element, you can use the break-inside property. This can be useful when you want to ensure that an element, such as a paragraph or a div, is not split across two pages.
CSS for avoiding breaks inside elements
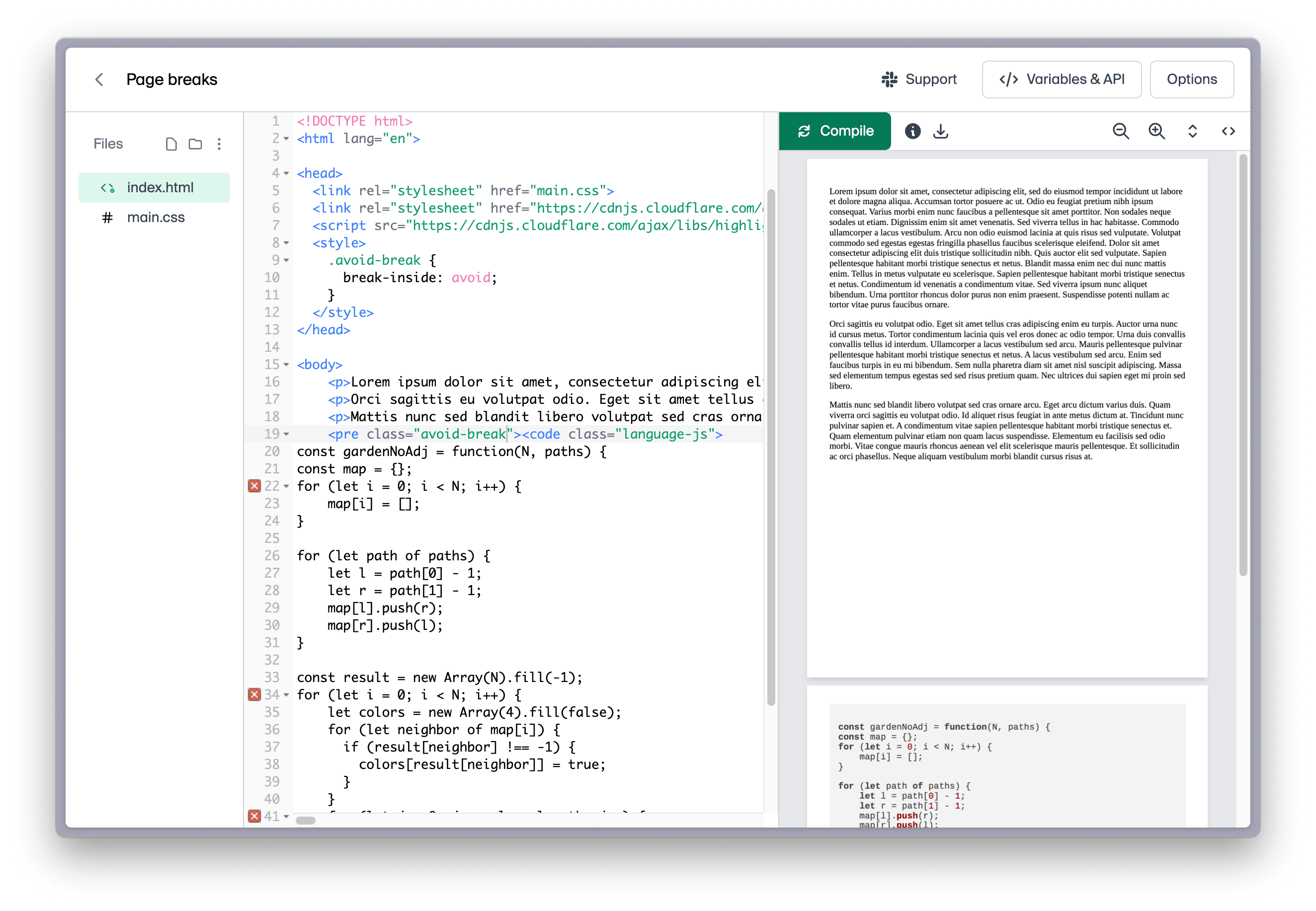
.avoid-break {
break-inside: avoid;
}
In the above example, a page break will be avoided inside each element with the .avoid-break class.
Without break-inside: avoid
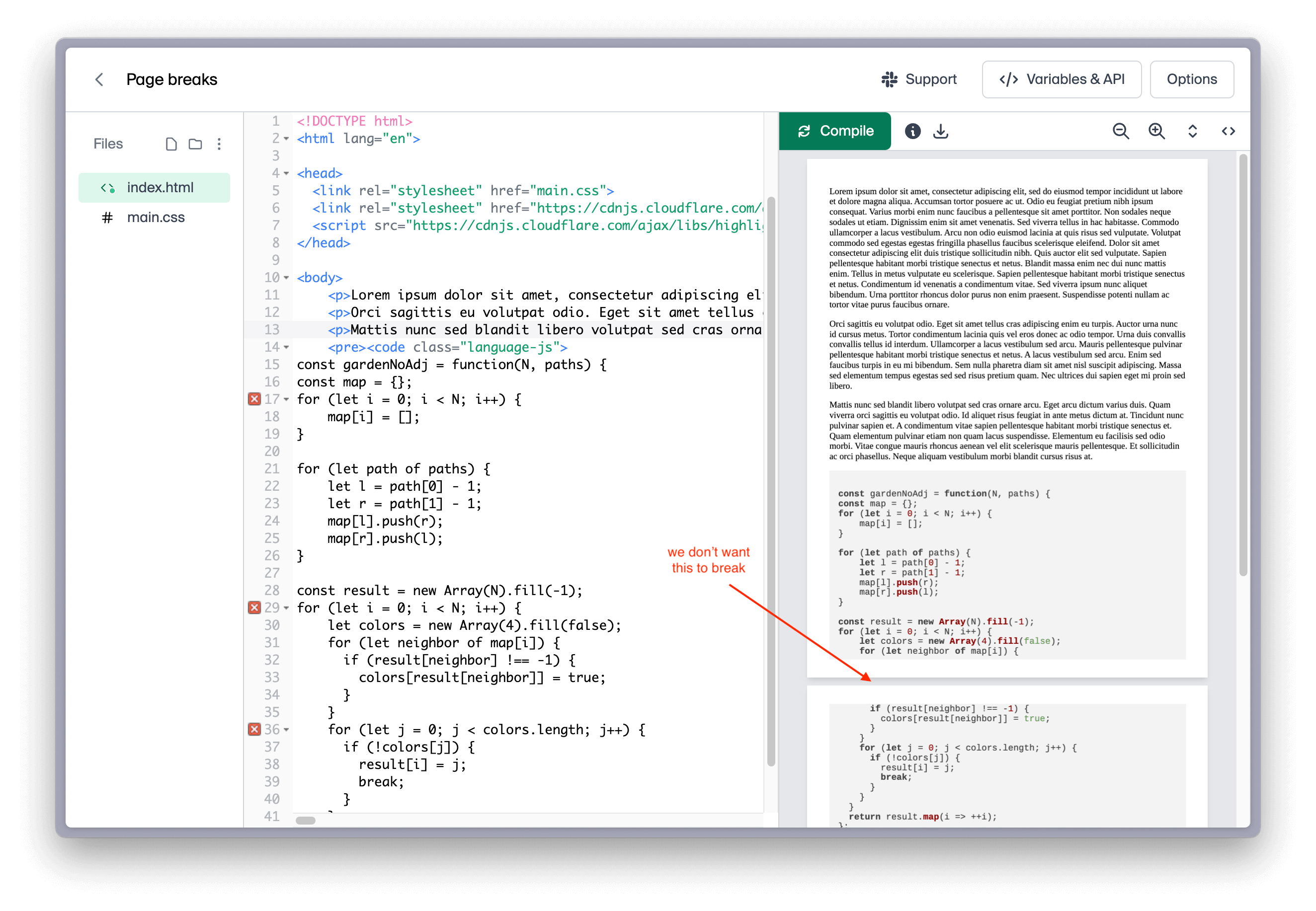
With break-inside: avoid